Indoor air quality (IAQ) is a critical factor in maintaining a healthy and safe environment, whether in homes, offices, or industrial settings. Among the various gases that can affect air quality, ammonia (NH3) is a common pollutant that poses health risks when present in high concentrations. An NH3 sensor plays a vital role in detecting and monitoring ammonia levels, ensuring a safer indoor atmosphere.
This article explores the importance of NH3 sensors in indoor air quality monitoring, their working principles, applications, and how they contribute to a healthier living and working environment.

Why Is Ammonia (NH3) a Concern for Indoor Air Quality?
Ammonia is a colorless gas with a sharp, pungent odor, commonly found in cleaning products, fertilizers, refrigeration systems, and industrial processes. While low levels of ammonia are generally not harmful, prolonged exposure or high concentrations can lead to:
Respiratory irritation (coughing, throat discomfort)
Eye and skin irritation
Headaches and dizziness
Aggravation of asthma and other lung conditions
In extreme cases, very high ammonia levels can cause severe lung damage or even be fatal. This makes continuous monitoring essential, especially in enclosed spaces where ventilation may be limited.
How Does an NH3 Sensor Work?
An NH3 sensor detects and measures ammonia concentrations in the air using different technologies, including:
1. Electrochemical Sensors
These gas sensors generate an electrical signal proportional to the ammonia concentration when NH3 molecules react with an electrode. They are highly sensitive and suitable for real-time monitoring.
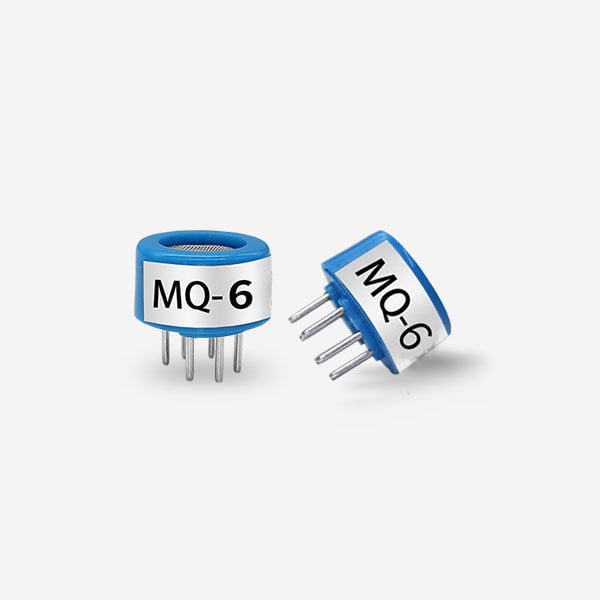
2. Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) Sensors
MOS gas sensors change their electrical resistance when exposed to ammonia, providing a cost-effective solution for continuous air quality monitoring.
3. Optical Sensors
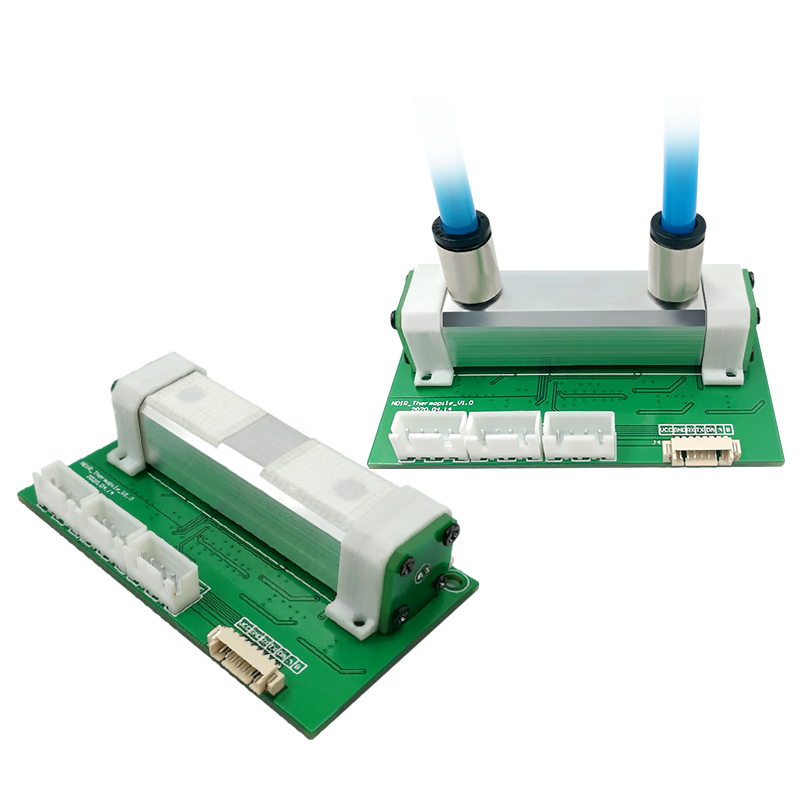
Using infrared (IR) or laser-based detection, these sensors measure ammonia by analyzing light absorption patterns, offering high accuracy for industrial applications.
Each type of NH3 sensor has its advantages, depending on the required sensitivity, response time, and environmental conditions.

Key Applications of NH3 Sensors in Indoor Air Quality Monitoring
1. Residential and Commercial Buildings
Ammonia can accumulate indoors from cleaning agents, pet waste, or building materials. An NH3 sensor helps homeowners and facility managers ensure safe air quality levels.
2. Agricultural Facilities
Farms and livestock barns often have high ammonia emissions due to animal waste. Sensors help maintain healthy conditions for both workers and animals.
3. Industrial and Manufacturing Plants
Industries using ammonia in refrigeration, chemical production, or wastewater treatment rely on NH3 sensors to prevent hazardous leaks.
4. Laboratories and Healthcare Facilities
Ammonia is used in various medical and research applications. Sensors ensure safe handling and storage to protect staff and patients.
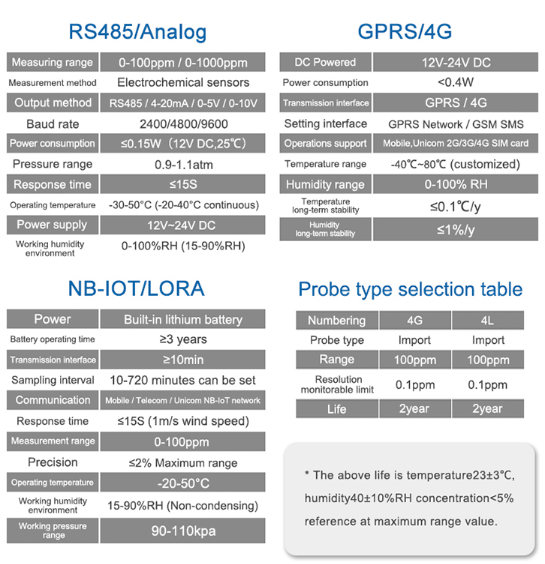
Benefits of Using an NH3 Sensor for Indoor Air Quality
Early Leak Detection – Prevents dangerous ammonia buildup before it reaches harmful levels.
Regulatory Compliance – Helps industries meet workplace safety standards (OSHA, NIOSH).
Health Protection – Reduces risks of respiratory and skin-related health issues.
Energy Efficiency – Smart sensors can integrate with HVAC systems to improve ventilation when needed.
Conclusion
An NH3 sensor is a crucial tool for maintaining safe indoor air quality by detecting ammonia leaks early and preventing health hazards. Whether in homes, farms, or industrial settings, these sensors provide reliable monitoring to ensure a healthier environment.
Investing in a high-quality NH3 sensor not only enhances safety but also contributes to regulatory compliance and long-term cost savings by preventing ammonia-related risks. For optimal air quality management, consider integrating NH3 detection into your indoor safety systems today.